
Business 3 - Phlox Elementor WordPress Theme
Complete Elementor Demo - Phlox WordPress Theme
GIZ
Study on Blockchain in Disaster Management
India
Innovation in Disaster Management & Climate Resilience


About The Project
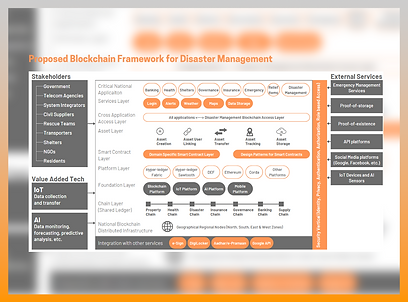
The Blockchain Applications in Disaster Management & Climate Resilience study was undertaken under the TUEWAS (Transport, Environment, Energy, and Water in Asia) platform, fostering regional cooperation among GIZ entities globally. The initiative focused on exploring the transformative potential of blockchain and emerging digital technologies within disaster management systems in India. Commissioned by the GIZ India Urban Team, Urban Innovation Lab was engaged to conduct a pioneering baseline study examining how blockchain, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and data-driven platforms could strengthen disaster resilience in urban ecosystems. The study was aligned with the Sustainable Urban Development – Smart Cities (SUD-SC II) initiative, particularly within partner states including Kerala, Odisha, and Telangana. The project sought to bridge the gap between technological theory and on-ground implementation by identifying scalable, practical, and contextually relevant digital solutions. By analyzing disaster response mechanisms and operational processes, the study aimed to create a replicable framework for Indian cities to enhance preparedness, response efficiency, transparency, and long-term climate resilience.Services Provided
The engagement covered end-to-end research, stakeholder consultations, case study development, strategic analysis, and formulation of an implementation-oriented digital resilience framework.Stakeholder Engagement & Insight Gathering
Over 20 structured online consultations were conducted with private sector IT firms, blockchain solution providers, disaster management professionals, and implementation agencies across India. These consultations generated practical insights on feasibility, technological readiness, governance barriers, and integration challenges.Extensive Secondary Research & Global Benchmarking
A rigorous review of 50+ global case studies and 120+ research papers was undertaken, covering sectors such as transportation, energy systems, humanitarian supply chains, climate resilience, and digital governance. The research established a comprehensive knowledge base to contextualize blockchain applications in disaster risk reduction.Case Study Development
Six detailed case studies were developed to demonstrate real-world applications of blockchain technology, including:- E-Governance Blockchain for Emergency Response – Bhopal Smart City
- Digital Asset Record Systems for Marginalized Communities – Nepal
- World Food Programme’s “Building Blocks” for Cash Transfer Efficiency
- Blockchain-Based Medical Supply Chain Tracking during COVID-19
- E-Wallet Systems for Donations & Emergency Insurance
- Blockchain-Enabled Land Registry Systems in India